Step into the information age, where mapping tools have revolutionised navigation. The evolution from traditional paper maps to dynamic web platforms is nothing short of extraordinary. Here on our blog, we introduce you to ùmap, a versatile tool for mapping, data visualisation, and geographical analysis.
Join us as we delve into how Ùmap is reshaping the landscape of mapping technologies, unlocking endless possibilities!
Evolution of Mapping: From Paper Maps to Digital Platforms
Mapping has undergone a remarkable evolution over the centuries, transitioning from traditional paper-based maps to dynamic digital platforms that revolutionize how we interact with spatial data.
This transformation has been driven by advancements in technology, ranging from Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) applications, fundamentally changing how maps are created, utilized, and understood.
The Rise of Versatile Mapping Technologies:
In the past, maps were primarily static representations, limited in their ability to convey real-time data and complex spatial relationships. With the advent of digital mapping technologies, such as GIS, maps have become dynamic tools that integrate various layers of information.
GIS, for instance, enables the overlaying of geographical data with demographic, environmental, and economic data, allowing for sophisticated spatial analysis and decision-making.
This capability has revolutionized fields like urban planning, environmental management, agriculture, and emergency response by providing planners and decision-makers with detailed insights into spatial relationships and trends.
Types of ùmap:
1. Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS is at the forefront of modern mapping technology, providing robust tools for capturing, analyzing, and visualizing spatial data.
It allows users to create maps that incorporate multiple data layers, such as topography, land use, population density, and infrastructure.
GIS applications are diverse, from mapping natural resource distributions to analyzing crime patterns in urban areas.
The versatility of GIS has made it indispensable across various industries, supporting everything from disaster response operations to precision agriculture.
2. Virtual and Augmented Reality Maps:
Virtual and augmented reality have introduced immersive mapping experiences that blur the lines between physical and digital environments.
VR maps overlay digital information onto a user’s view of the real world, enhancing navigation, tourism experiences, and architectural design.
AR maps, on the other hand, integrate digital elements into the user’s physical surroundings, offering interactive and contextual information.
These technologies are transforming how we explore and interact with geographical spaces, offering new perspectives and enhancing user engagement in fields like education, gaming, and urban planning.
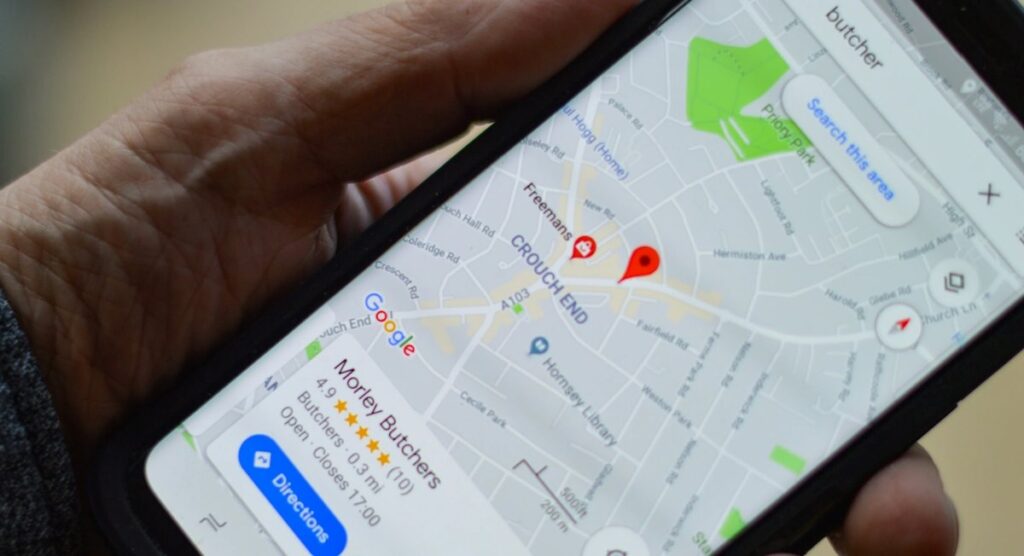
3. Interactive Web ùmaps:
Interactive web maps have democratized access to geographical information, making maps accessible through web browsers and mobile devices.
Platforms like Google Maps and OpenStreetMap allow users to search for locations, obtain directions, and explore detailed information about businesses, landmarks, and points of interest.
These maps leverage cloud computing and responsive design to deliver real-time updates and personalized experiences, catering to diverse user needs from navigation to social mapping applications.
Advantages of Using ùmap:
Modern mapping technologies offer several advantages over traditional paper maps:
- Accessibility: Digital maps are accessible anytime, anywhere, through a variety of devices, facilitating seamless navigation and information retrieval.
- Real-Time Updates: Digital platforms can update maps instantly with new data, ensuring users have access to the latest information on traffic conditions, weather patterns, and infrastructure changes.
- Data Integration: GIS and other digital mapping tools integrate multiple data sources, allowing for comprehensive analysis and informed decision-making across sectors.
- Visualization: Advanced mapping technologies enhance spatial visualization, making complex data more understandable and actionable for users ranging from researchers to policymakers.
Applications in Various Industries:
Mapping technologies have diverse applications across industries:
- Urban Planning: City planners use GIS to analyze demographic trends, plan transportation networks, and optimize land use, contributing to sustainable urban development.
- Environmental Management: GIS supports environmental monitoring, habitat conservation, and natural resource management by mapping ecological patterns, monitoring pollution levels, and predicting environmental impacts.
- Transportation: Navigation apps utilize real-time mapping to provide accurate routing information, optimize traffic flow, and improve transportation logistics.
- Healthcare: Spatial analysis in healthcare facilitates disease mapping, resource allocation, and epidemiological studies, aiding in the management of public health crises and healthcare delivery.
Challenges and Limitations:
Despite their advantages, digital mapping technologies face challenges that include:
- Data Quality: Ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and completeness of spatial data remains a challenge, impacting the effectiveness of mapping applications.
- Privacy Concerns: Handling sensitive location data requires robust privacy policies and security measures to protect user information.
- Technological Barriers: Access to advanced mapping tools and technical expertise may be limited in certain regions, hindering widespread adoption and utilization.
Future Developments and Innovations:

The future of mapping is poised for further innovation and integration with emerging technologies:
- Artificial Intelligence: AI-driven mapping solutions will enhance data processing, pattern recognition, and predictive modeling capabilities, improving the accuracy and efficiency of spatial analysis.
- Sensor Integration: Advances in sensor technology, including IoT devices and satellite imaging, will enhance data collection and spatial resolution, enabling real-time monitoring and analysis of environmental changes.
- Augmented Reality: AR-enabled mapping applications will continue to enhance user experiences by overlaying real-time data onto physical environments, transforming how individuals interact with spatial information.
FAQ’s
1. What drove the evolution from paper maps to digital platforms?
Advancements in technology, including GIS and VR/AR applications, enabled real-time data integration and enhanced spatial analysis capabilities.
2. What are GIS and how do they enhance mapping?
GIS (Geographic Information Systems) are tools for capturing, analyzing, and visualizing spatial data, integrating multiple layers like demographics and infrastructure to support informed decision-making.
3. How do virtual and augmented reality maps differ?
VR maps offer immersive experiences by overlaying digital information on a user’s view, while AR maps integrate digital elements into the user’s physical surroundings for interactive information.
4. What are interactive web maps, and why are they significant?
These maps, like Google Maps, offer accessible navigation and detailed information via web browsers and mobile devices, leveraging real-time updates and personalized experiences.
5. What advantages do digital maps offer over traditional paper maps?
Accessibility from anywhere, real-time updates, data integration for comprehensive analysis, and enhanced visualization of complex spatial data.
6. In which industries are mapping technologies widely used?
Urban planning, environmental management, transportation, healthcare, and more benefit from GIS and digital mapping for planning, monitoring, and resource allocation.
7. What challenges do digital mapping technologies face?
Challenges include ensuring data quality, managing privacy concerns with sensitive location data, and overcoming technological barriers to widespread adoption.
8. What innovations can we expect in the future of mapping?
AI-driven solutions for enhanced data processing, sensor integration for real-time monitoring, and continued advancements in AR applications for interactive spatial experiences.
Conclusion
The evolution of mapping from paper-based maps to dynamic digital platforms has revolutionized how we perceive, analyze, and interact with geographical data. Modern mapping technologies like GIS, virtual reality maps, and interactive web maps have expanded the possibilities for spatial analysis, decision-making, and user engagement across industries. As these technologies continue to evolve and integrate with emerging innovations, the future of mapping holds immense potential to address global challenges, enhance sustainability efforts, and empower individuals and organizations with actionable spatial insights. Embracing these advancements in mapping is key to navigating an increasingly interconnected and data-driven world effectively.
Also Read:





