Introduction:
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on milialar, commonly known as milia. These small, white bumps can appear on the skin, often causing concern for those who discover them. In this article, we’ll explore what milia are, where they commonly appear, how they form, different types, treatment and prevention methods, how they differ from acne, and effective home remedies. Let’s dive in to understand and manage milia better.
What Are Milialar (Milia)?
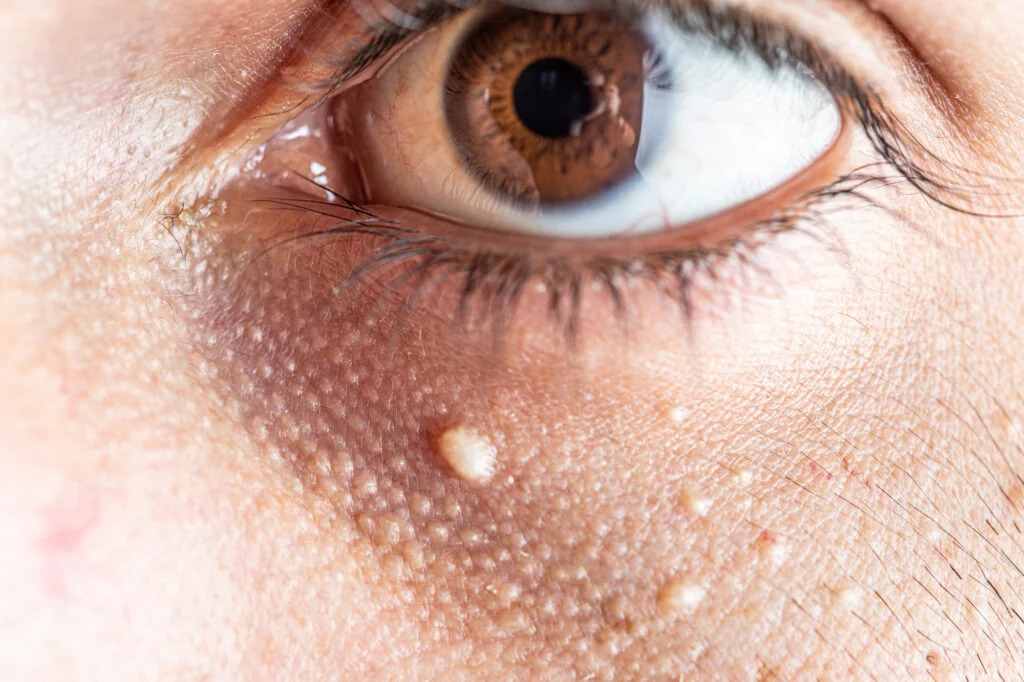

Milialar, or milia, are tiny cysts that form on the skin, filled with keratin—a protein found in skin cells. They appear as small, white or yellowish bumps and are usually harmless. Milia can occur at any age and are particularly common in newborns, though they can affect individuals of all ages.
Where Do They Appear?
Milia commonly appear on the face, particularly around the eyes, cheeks, nose, and forehead. They can also occur on other parts of the body, including the torso and limbs. In newborns, milia often appear on the nose and cheeks but can resolve on their own without treatment.
How Do They Form?
Milia form when dead skin cells become trapped beneath the skin’s surface instead of naturally shedding. This entrapment creates small cysts filled with keratin. Several factors can contribute to the formation of milia, including skin damage, sun exposure, heavy skincare products, and certain medical conditions.
Types of Milialar:
There are several types of milia, each differing slightly in their cause and appearance:
- Primary Milia: Commonly found in infants, but also in adults, these form spontaneously without any clear cause.
- Secondary Milia: These develop due to skin trauma, such as burns, blisters, or procedures like dermabrasion.
- Neonatal Milia: A type of primary milia occurring in newborns, usually on the face and scalp.
- Juvenile Milia: Associated with genetic conditions, these appear in children and are linked to inherited disorders.
- Milia en Plaque: Characterized by patches of milia on inflamed, raised areas of skin, often associated with autoimmune diseases.
Also read: A Story About Sitting Next To A Scary Yakuza – Beyond Stereotypes and Scary Stories!
Treatment and Prevention:
While milia are generally harmless and may resolve on their own, treatment options are available for those who wish to remove them:
Treatment Options:
- Topical Retinoids: These can help exfoliate the skin and prevent the formation of new milia.
- Extraction: Performed by a dermatologist, this involves using a sterile needle to remove the milia.
- Chemical Peels: These can help to remove the top layer of skin, aiding in milia treatment.
Prevention Tips:
- Gentle Exfoliation: Regular, gentle exfoliation can prevent dead skin cells from becoming trapped.
- Sun Protection: Using sunscreen can prevent sun damage, which can contribute to milia formation.
- Non-Comedogenic Products: Use skincare products that do not clog pores.
Milialar vs. Acne:

Milia and acne can appear similar but have distinct differences:
- Milia: Small, white cysts filled with keratin, not typically inflamed, and usually painless.
- Acne: Includes various forms such as blackheads, whiteheads, pimples, and cysts, often inflamed and sometimes painful.
Understanding these differences is crucial for proper treatment and management.
Home Remedies for Milialar:
Several home remedies can help manage and potentially reduce milia:
- Honey: Known for its antibacterial properties, applying honey can help soothe the skin.
- Aloe Vera: Its soothing and healing properties can aid in reducing inflammation and promoting skin health.
- Steam: Facial steaming can open up pores, making it easier for milia to be released naturally.
- Sugar Scrubs: Gentle sugar scrubs can exfoliate the skin, helping to remove dead skin cells.
FAQ’s
1. What are milialar (milia)?
Milialar, or milia, are small cysts filled with keratin that appear as white or yellowish bumps on the skin. They are typically harmless.
2. Where do milia commonly appear?
Milia commonly appear on the face, especially around the eyes, cheeks, nose, and forehead. They can also occur on the torso and limbs.
3. How do milia form?
Milia form when dead skin cells become trapped beneath the skin’s surface, creating small cysts filled with keratin. Factors like skin damage, sun exposure, and heavy skincare products can contribute to their formation.
4. What are the different types of milia?
There are several types, including primary milia (common in infants and adults), secondary milia (due to skin trauma), neonatal milia (in newborns), juvenile milia (linked to genetic conditions), and milia en plaque (associated with autoimmune diseases).
5. How can milia be treated?
Treatment options include topical retinoids, professional extraction by a dermatologist, and chemical peels. These methods help remove existing milia and prevent new ones from forming.
6. Can milia be prevented?
Preventative measures include gentle exfoliation, using sunscreen to prevent sun damage, and choosing non-comedogenic skincare products that do not clog pores.
7. How are milia different from acne?
Milia are small, white cysts filled with keratin that are not inflamed and usually painless. Acne includes various forms like blackheads, whiteheads, pimples, and cysts, which are often inflamed and can be painful.
8. What home remedies can help with milia?
Effective home remedies include applying honey for its antibacterial properties, using aloe vera for its soothing and healing effects, facial steaming to open up pores, and using gentle sugar scrubs for exfoliation.
9. Are milia harmful?
No, milia are generally harmless and often resolve on their own. However, some people opt for treatment due to cosmetic concerns.
10. Can milia reoccur after treatment?
Yes, milia can reoccur, especially if preventative measures are not followed. Regular exfoliation, sun protection, and using appropriate skincare products can help reduce the likelihood of recurrence.
Conclusion
Milia, though harmless, can be a cosmetic concern for many. Understanding what milia are, where they appear, and how they form can help in managing and preventing these small cysts. Various treatment options, both professional and home remedies, can effectively address milia. By incorporating preventative measures and understanding the differences between milia and other skin conditions like acne, you can maintain healthy, clear skin.
Related Post: